Elabscience Assay Kits
Elabscience Assay Kits
Manufacturer: Elabscience
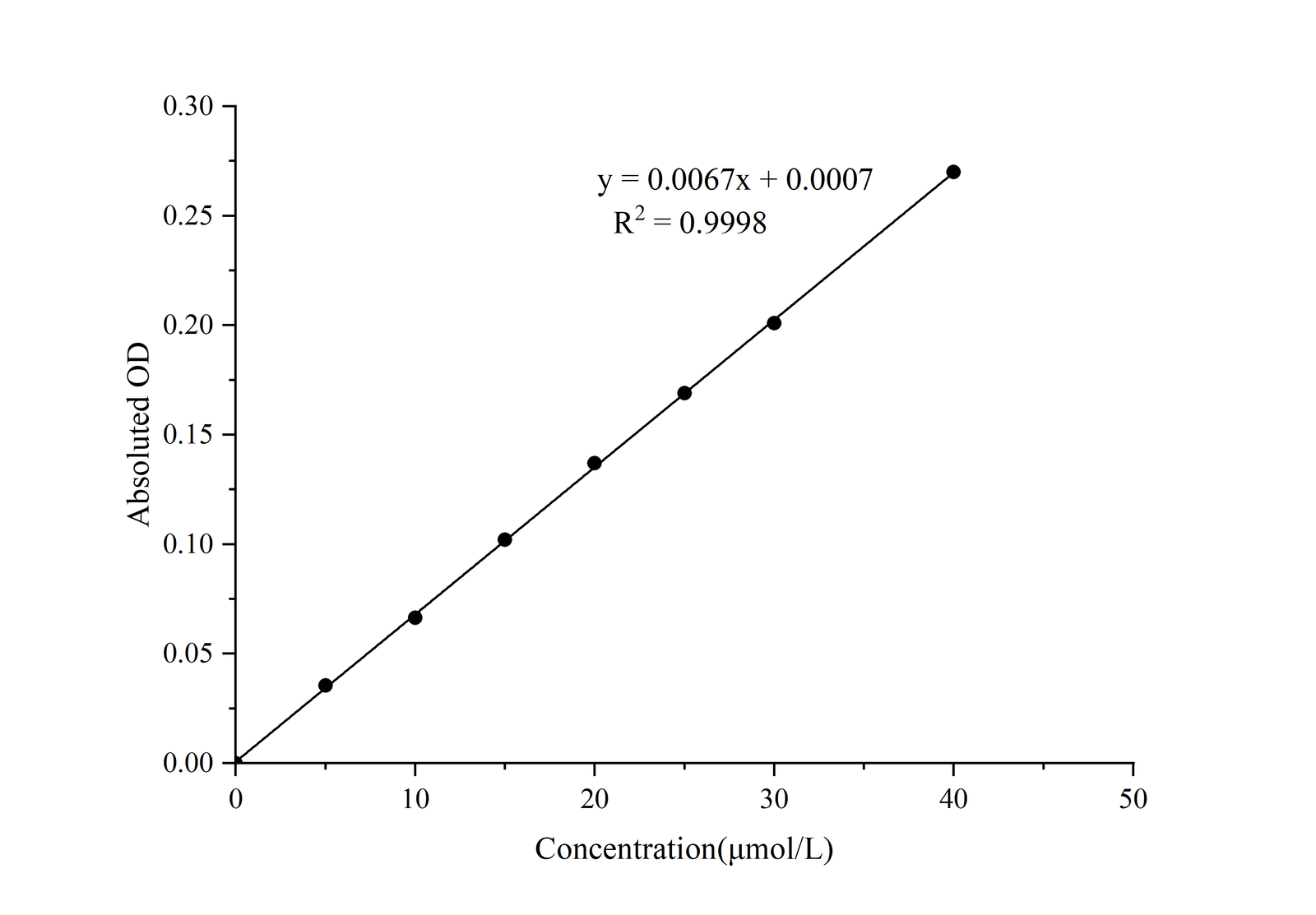
Succinic acid, also known as succinic acid, is widely present in all plant and animal tissues, was first extracted from amber, is an intermediate in the citric acid cycle, and plays an important role in the production of energy in cells. Succinate, or succinate, is widely used in the agricultural, food and pharmaceutical industries due to its low toxicity. Succinic acid is catalyzed by enzyme reagent to form colored substance with color developer. The maximum absorption is at 555 nm. The content of succinic acid in samples can be calculated by measuring OD value and standard curve at 555 nm.
Manufacturer: Elabscience
Oxaloacetic acid (OAA), one of the intermediates in the tricarboxylic acid cycle is an important substance in carbon and nitrogen metabolism. Oxaloacetate reacts with substrate acetyl-coA under the action of enzyme. The substance produced can react with DTNB, which has the maximum absorption peak at 412 nm. The content of oxaloacetate can be determined by measuring the absorbance value.
Manufacturer: Elabscience
As an organelle, mitochondria is the "power factory" in cells and the main site of aerobic respiration of cells. Its function is to convert energy through oxidative phosphorylation to provide energy for cellular activities. The oxidation process is carried out by four respiratory chain membrane protein complexes (complexes I, II, III and IV) on the inner mitochondrial membrane. Mitochondrial complex III, also known as cytochrome c reductase complex, its main function is to oxidize the reduced coenzyme Q10 formed by mitochondrial complexes I and II to oxidative coenzyme Q10. In this process, the OD value increased at 550 nm. Therefore, the activity of mitochondrial complex III can be quantified by measure the change OD value at 550 nm.
Manufacturer: Elabscience
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) is a high-energy phosphate compound, which is the most direct energy source in the body, and its content is directly related to the state of energy metabolism in the body. Hexokinase (HK) catalyzes the generation of glucose and ATP into glucose-6-phosphate, and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) further catalyzes the dehydrogenation of glucose-6-phosphate into NADPH. NADPH can react with the color developer, and the product has a characteristic absorption peak at 460 nm to determine the ATP content.
Manufacturer: Elabscience
Glutamine synthetase (GS) is one of the central enzymes in nitrogen metabolism With ATP consumption, GS catalyzes glutamate to produce glutamine. The latter is an amino donor of various nitrogenous substances such as proteins, nucleic acids and various coenzymes. As a conditionally essential amino acid for the human body, the production of glutamine has received extensive attention in recent years. GS catalyzes ammonium ion and glutamic acid to synthesize amide, and produces chromogenic substance under the action of invertase and chromogenic agent. The maximum absorption peak is at 570 nm. The activity of GS in samples is calculated by measuring OD value at 570 nm and standard curve.
Manufacturer: Elabscience
Aconitase (ACO) is an important Fe/S protein enzyme in cells, which mainly exists in cytoplasm and mitochondria. ACO catalyzes the reversible reaction of citric acid to isocitric acid from the intermediate product cisaconite acid in the cell, which plays an important role through maintaining the tricarboxylic acid cycle and glyoxylic acid cycle. Aconitase catalyzes isocitrate to produce cis-aconitase. Cis-aconitase has a characteristic absorption peak at 240 nm. The activity of this enzyme was calculated by measuring the production rate of cis-aconitase.
Manufacturer: Elabscience
Abnormal accumulation of cellular cuprous in cells induces the oligomerization of key components of the lipoic acid-modified pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, which affects the tricarboxylic acid cycle, triggers proteotoxic stress, and induces cell death. Cellular cuprous can catalyze the substrate to produce fluorescent substances, and the higher the copper ion concentration, the more fluorescent substances are generated per unit time. The fluorescence delete can be detected at the excitation wavelength of 395 nm and emission wavelength of 480 nm.
Manufacturer: Elabscience
Glycolysis is an important ATP generation pathway in eukaryotic cells. Glycolytic stress testing can directly measure the extracellular acidification rate (ECAR) to evaluate the changes of glycolytic process in living cells, and can obtain key parameters for a comprehensive assessment of glycolytic pathway, including: glycolysis, glycolytic capacity, glycolytic reserve and non-glycolytic acidification. This kit uses 2-deoxy-D-glucose (2-DG) and oligomycin to facilitate in-depth analysis of cellular glycolytic flux: 2-DG quantifies nonglycolytic extracellular acidification (ECA) by blocking glycolysis through competitive hexokinase inhibition; Oligomycin inhibits ATP synthetase and therefore prevents aerobic ATP production, forcing the cell to increase glycolytic flux to meet ATP demand. Such compensatory glycolysis levels achievable under the test conditions could reveal glycolytic perturbations that are not apparent under basal conditions and help assess glycolytic capacity with limited ATP demand.
Manufacturer: Elabscience
Ferroptosis inhibitory protein-1(FSP-1) induce non-caspase-dependent apoptosis based on factors such as C-terminal fragment of amino acid series, nuclear translocation and overexpression. Through the FSP1-CoQ10-NAD(P)H pathway and the classical glutathione (GSH)-GPX4 pathway, FSP-1 can protect cells from ferroptosis, and plays a "double-edged sword" role in cell life activities. The detection principle of this kit: FSP-1 catalyzes the substrate reaction to generate NADH, so that its fluorescence value increases under the excitation wavelength of 535 nm and emission wavelength of 587 nm. Adding inhibitors will inhibit the activity of FSP-1 and cause the rate of increase in fluorescence value to decrease, and the activity of FSP-1 can be calculated by measuring the difference value.